Learning how to exercise with arthritis can be challenging, but with these tips for managing joint pain you can significantly improve the exercise experience and overall mobility. The correct exercises and techniques can help manage arthritis symptoms and enhance your quality of life. Let’s find effective exercise methods for arthritis and maintain an active lifestyle.

Understanding Arthritis and its Impact on Exercise
Before delving into specific exercises, it’s crucial to understand arthritis and its effects on the body. Arthritis is a condition known for joint inflammation that leads to pain, stiffness, and reduced range of motion. Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis are the most well-known types, but prior injuries can also trigger arthritis symptoms regardless of age.
When exercising with arthritis, it’s essential to balance staying active and not exacerbating joint pain. Some exercises will not be suitable for everyone, (like running or jumping) because they can put additional stress on the joints. Instead, low-impact exercises are often recommended to minimize strain on the affected areas.
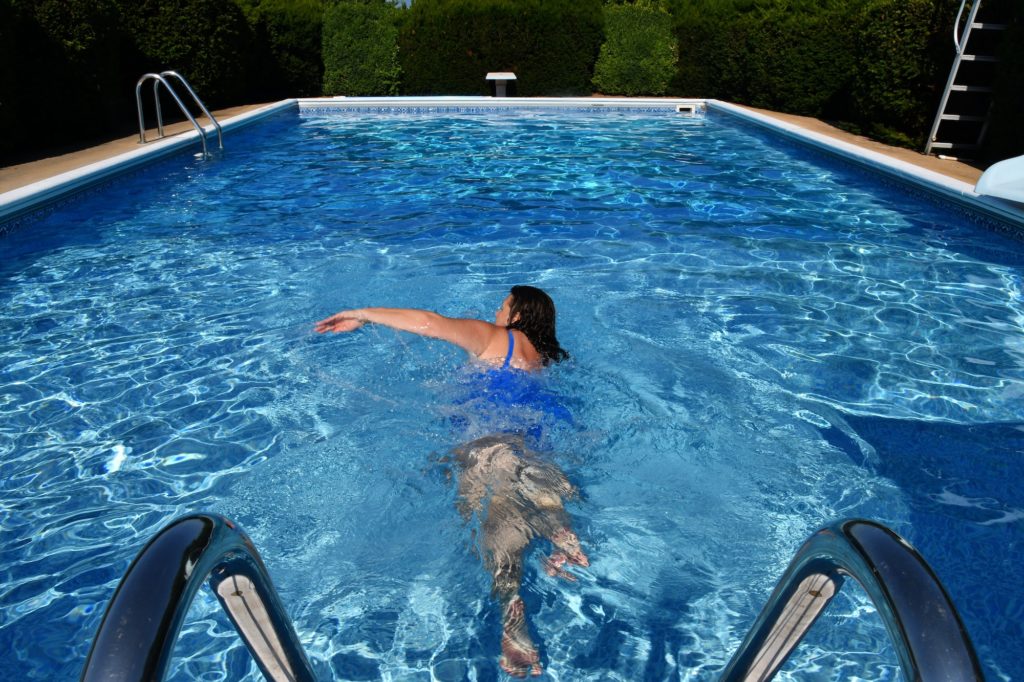

Low-Impact Aerobic Exercises for Arthritis
- Swimming: Swimming and water aerobics are excellent choices for people with arthritis. Water buoyancy helps reduce the impact on joints while providing a full-body workout. Swimming also helps improve range of motion and improve flexibility.
- Cycling: Cycling on a stationary or recumbent bike is an ideal low-impact exercise option. It strengthens leg muscles without putting excessive pressure on the joints.
- Walking: Walking is one of the most influential and straightforward exercises for arthritis. It is gentle on the joints and easily incorporated into your daily routine. Aim for at least 30 minutes of brisk walking daily to improve cardiovascular health and strengthen muscles around the joints.
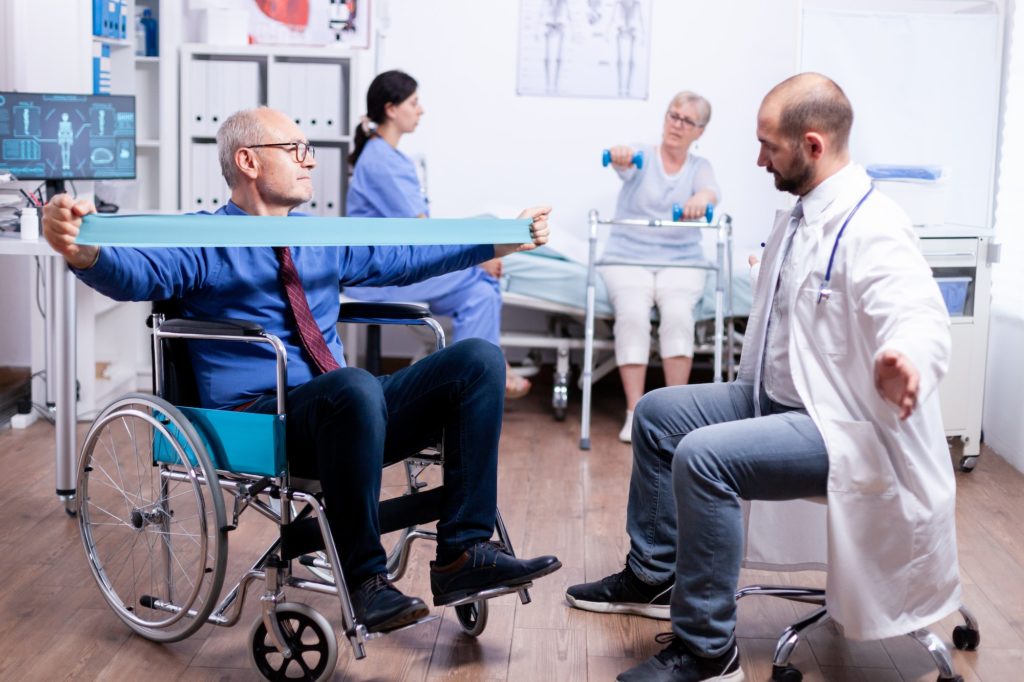
Strength Training for Arthritis
Building muscle strength is essential for supporting and stabilizing joints. However, when performing strength exercises with arthritis, it’s essential to use proper form and avoid putting too much strain on the affected areas.
- Resistance Bands: Using resistance bands can add resistance without causing excessive stress on the joints. They are versatile and can be adapted to any individual’s ability and fitness levels.
- Bodyweight Exercises: Bodyweight versions of squats, lunges, and modified push-ups can effectively strengthen muscles without needing weights. These exercises can also be adapted to individual ability and fitness levels.
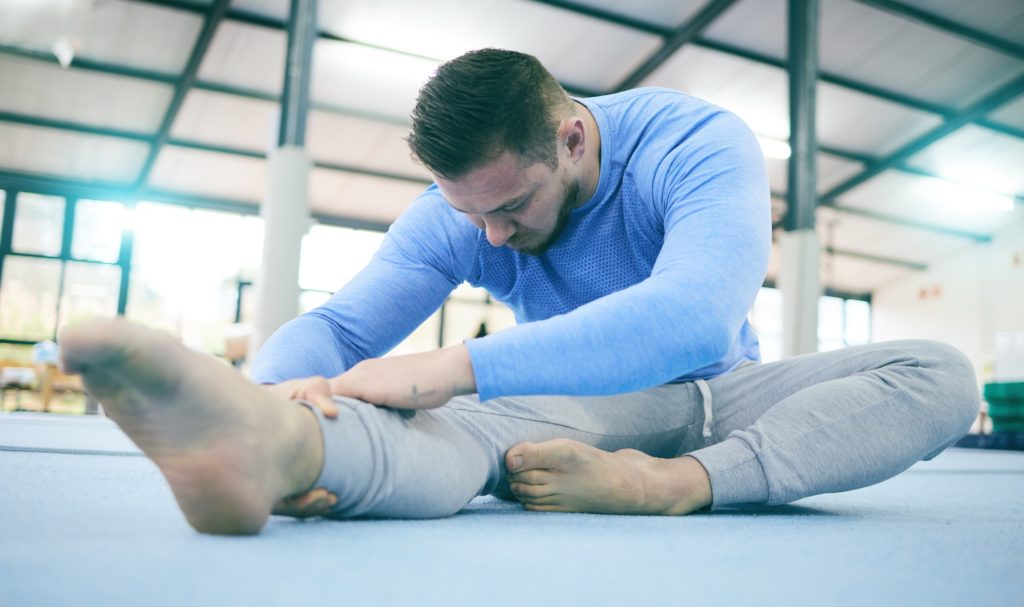

Flexibility and Stretching Exercises
Maintaining flexibility is crucial for arthritis sufferers to improve joint function and reduce stiffness.
1. Dynamic Stretching: Dynamic stretching is a fantastic way to enhance flexibility, balance, and strength. Many stretches can be modified to accommodate joint pain and mobility levels.
2. Pilates: Pilates is a popular and effective exercise method that focuses on strengthening the body’s core muscles, improving flexibility, and enhancing overall posture. It is known for its ability to build long, lean muscles, increase body awareness, and promote a sense of balance and harmony. It is also beneficial for individuals with arthritis to manage stress and enhance overall well-being.
Safety Tips for Exercising with Arthritis
While exercise is beneficial, it’s essential to exercise safely to avoid injury and exacerbation of arthritis symptoms.
- Check with Your Healthcare Practitioner: Consult your primary healthcare practitioner before beginning any exercise program, especially if you have severe arthritis or other medical conditions.
- Start Slowly: Begin with low-impact exercises and progressively increase the intensity and duration as your strength and endurance improve.
- Listen to Your Body: Be mindful of how your body responds to each movement. If you experience discomfort or pain, modify the exercises or take a rest day.
- Use Proper Gear: Wear supportive and comfortable shoes while exercising. If needed, use braces or splints to provide additional support to affected joints.
Suffering with arthritis doesn’t mean you should give up on staying active. Regular exercise, especially low-impact aerobic exercises, strength training, and flexibility exercises, can significantly improve joint pain and overall function. Remember: exercise safely, listen to your body, and consult your healthcare practitioner before starting any new exercise regimen. With dedication and the right approach, you can effectively manage arthritis and maintain an active and fulfilling lifestyle.



